But what exactly is search intent? Why is it so important for SEO? And how can an understanding of search intent help you rank higher in search engine result pages (SERPs)? These are the questions we’ll attempt to answer in this article. In this guide, we’ll cover:
What is Search Intent? Why is Search Intent Important? The Four Types of Search Intent How to Optimize Your Pages for Search Intent
Let’s get started.
What is Search Intent?
Search intent (also called user intent) is the goal behind every search query. It’s the reason why the user is typing a search query on Google.
What is Search Intent?Why is Search Intent Important?The Four Types of Search IntentInformational Search IntentCommercial Search IntentTransactional Search IntentNavigational Search IntentHow to Optimize Your Pages for Search Intent1. Analyze the search results for your target keywords2. Choose the right content type3. Update and relaunch existing content4. Improve the user experience on your website5. Get constant feedback from your communityFinal Thoughts
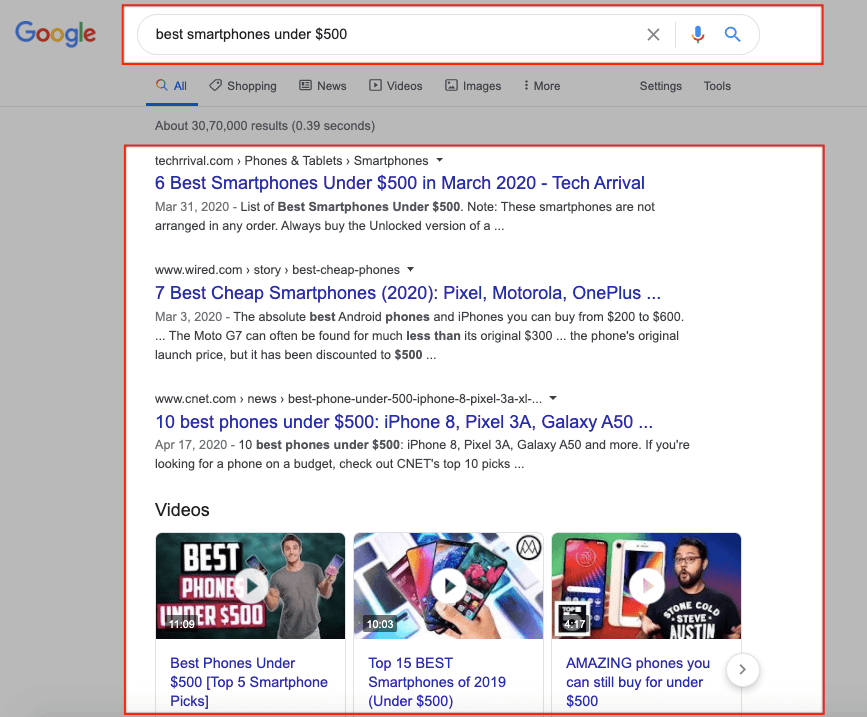
For example, when someone gives a search on “best smartphones under $500,” Google understands that the intent of the searcher is to learn more about the best smartphones within their specific budget. They are not looking for eCommerce category pages or product landing pages. They are looking for blog posts. Which is why the results on page 1 for this query are dominated by list posts featuring the best smartphones within the specified budget.
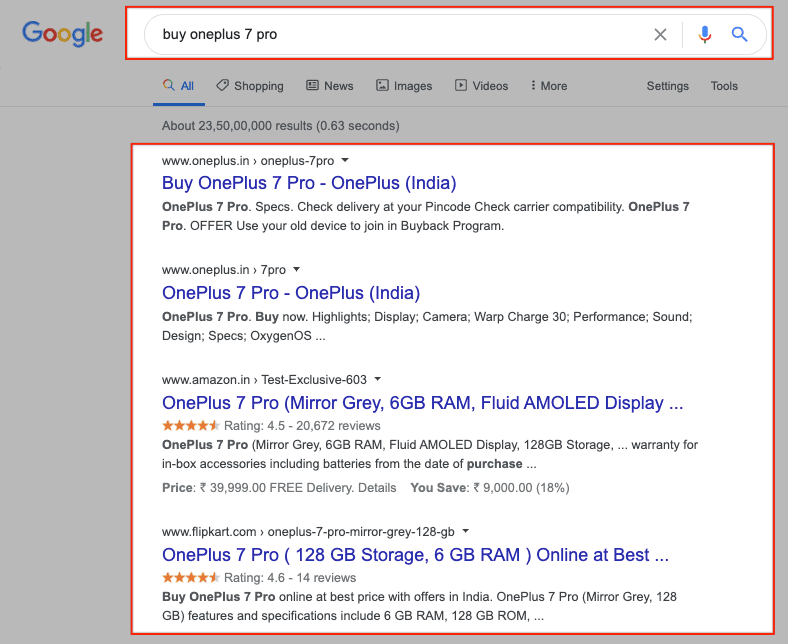
On the other hand, when someone searches for “buy oneplus 7 pro,” Google understands that the intent here is to buy. The specific user has already made up his/her mind to go with OnePlus 7 Pro. For that reason, the search results on page 1 for this query are eCommerce category pages or product pages where the user can make a purchase.
Why is Search Intent Important?
Google’s primary goal is to satisfy search intent. In other words, Google wants to provide the most relevant results to a particular search query.
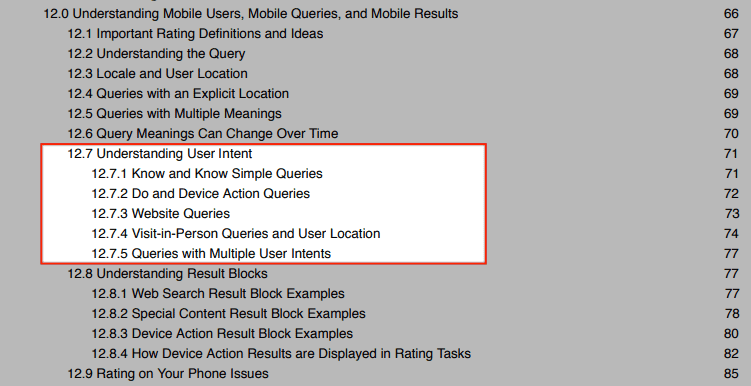
Google’s most recent edition of Search Quality Rater Guidelines dedicates quite a few pages to search intent. In fact, the phrase “user intent” is used 333 times in the document.
So, if you want your pages to rank higher in Google search results, you need to make sure that your content aligns with search intent.
The Four Types of Search Intent
There are four common types of search intent: Let’s explore each type of search intent in detail.
Informational Search Intent
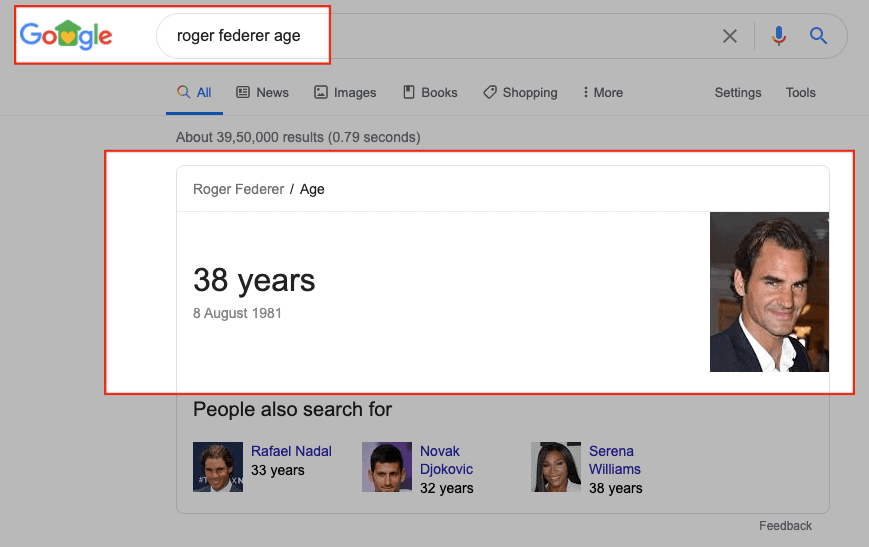
In this scenario, the user is searching for information. Google refers to informational search queries as “Know” queries. The information that the user is seeking may be an answer to a simple question like “what’s the time in Bangalore?” or it could be information on a complex topic like “Stoic philosophy.” Google further classifies searches that require a very specific answer as “Know Simple” queries. Search queries such as “roger federer age” and “microsoft stock price” demand an accurate and straightforward answer that can be displayed in a relatively small amount of space.
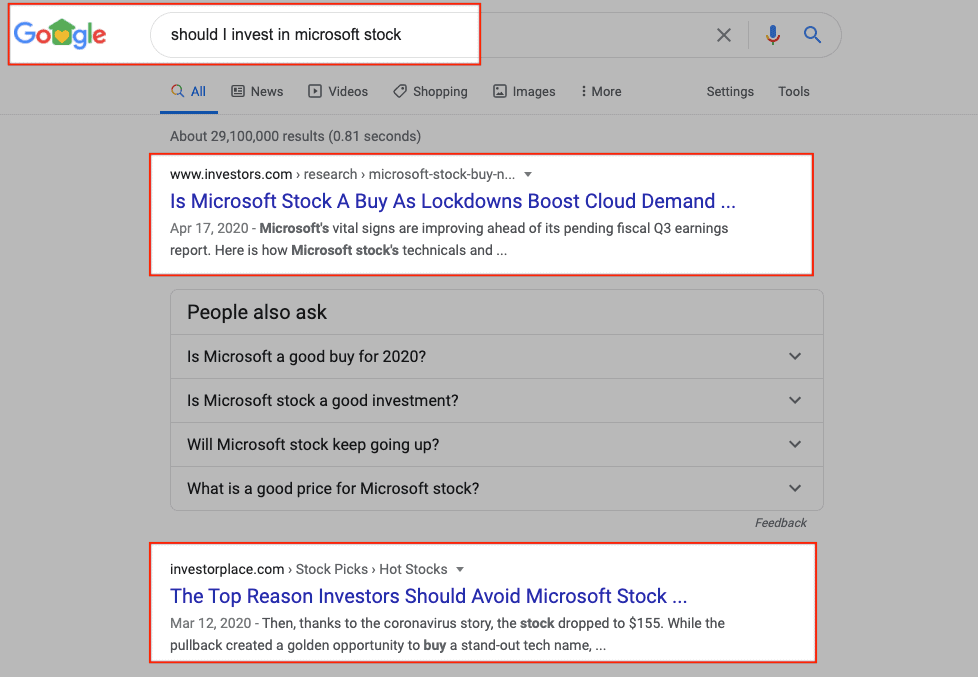
On the other hand, the “Know” query answers are more in-depth. For instance, a search query like “should I invest in microsoft stock” requires a more elaborate answer.
Here are some examples of informational search queries:
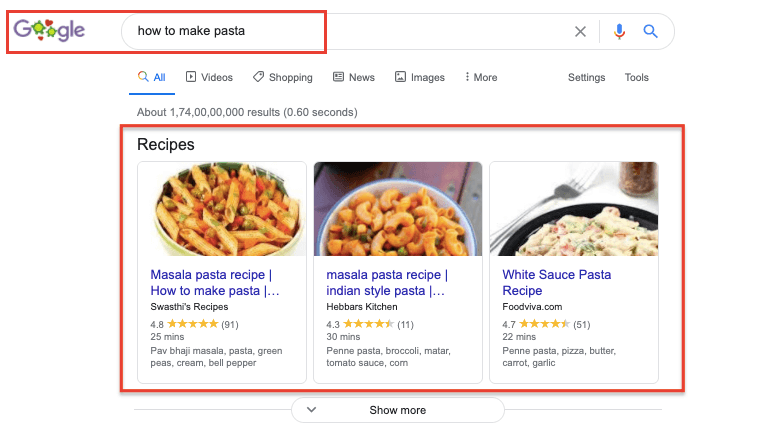
“bitcoin price” “how to play Fortnite” “how to make pasta” “content marketing” “Al Pacino” “how to meditate”
Commercial Search Intent
In this case, the user is interested in buying a product or a service but has not made up their mind yet. They are still undecided. They are most likely looking for a list of best products in a specific category or reviews and comparisons.
Examples of commercial search queries include:
“SEMrush vs Moz” “iPhone 11 pro review” “best headphones 2020” “ConvertKit review” “best PS4 games”
Transactional Search Intent
In this scenario, the user is looking to make a purchase. They have made up their mind to go for a specific product or service. As such, the page 1 results on Google are eCommerce category pages or product pages where the user can make the purchase.
Below are some examples of search queries with transactional intent:
“buy iPhone 11 pro” “Mailchimp price” “order food online” “buy macbook air 2020”
Navigational Search Intent
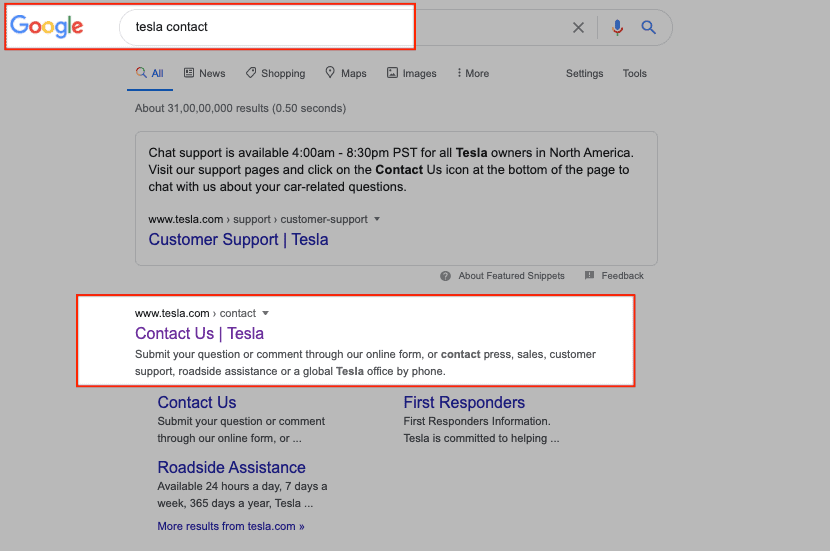
In this case, the searcher is looking for a specific website or webpage. Google refers to these queries as “Website” queries. The users already know where they’d like to go. For instance, users searching for “tesla contact” would like to visit the contact page of Tesla.
Examples of navigational queries include:
“LinkedIn” “SEMrush login” “technical SEO checklist 99signals” “washington post”
To summarize, here’s a quick reference guide to the four types of search intent:
How to Optimize Your Pages for Search Intent
Understanding the search intent behind your target keyword terms is one of the preliminary things you should do before you start creating content. Once you’ve determined the right search intent for your target keywords, here are 5 things you can do to optimize your content for search intent:
1. Analyze the search results for your target keywords
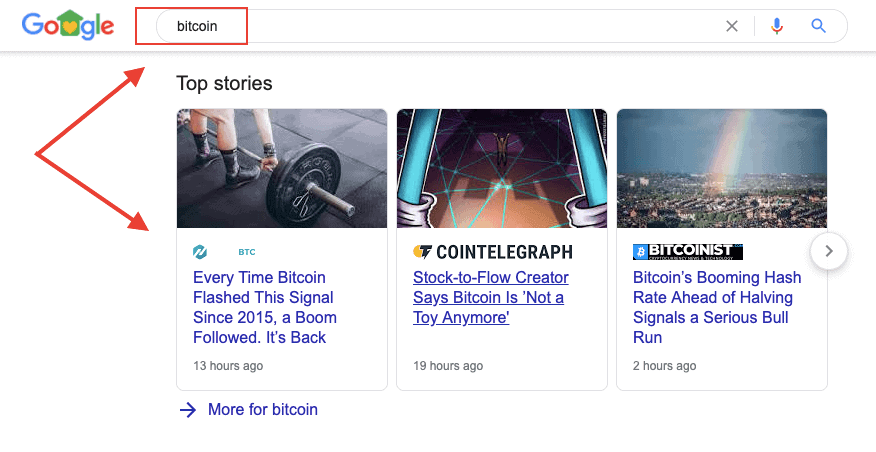
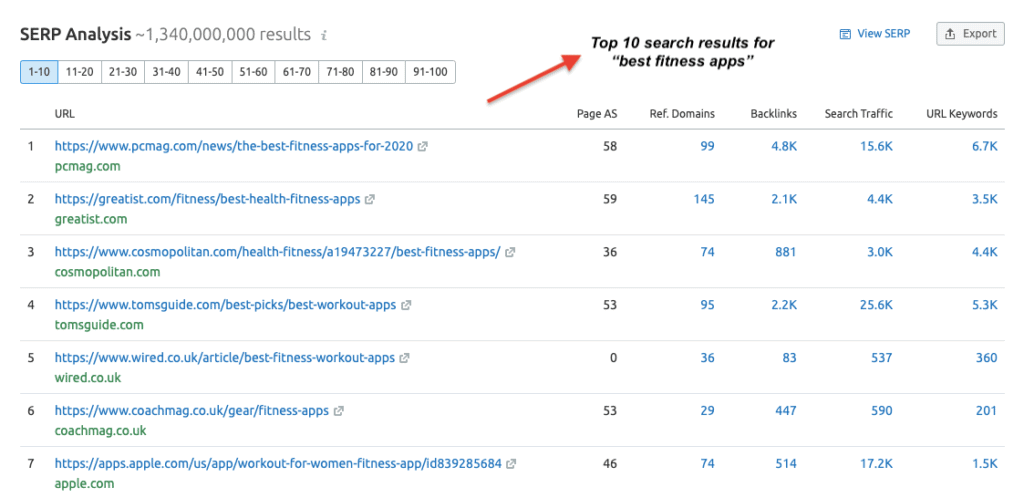
Perhaps the most important step in optimizing your content for search intent involves analyzing the top-ranking pages for your target keywords. Put differently, you need to deep dive into the SERPs to find out what pages are currently ranking for the topic you’re working on. You can do this by simply performing a Google search for the target keywords to see what results emerge. Just by looking at the top search results, you’ll most likely understand the search intent. In most cases, they will fall under one of the four types of search intent. In some cases, you’ll be able to identify the search intent for your target keywords(s) by looking at Google SERP features — a non-traditional organic result in Google search result pages. For instance, this “News Box” that appears on Google for “bitcoin” is a SERP feature.
The four most common SERP features are:
Rich Snippets (Reviews, Events, Recipes, etc.) Paid Results (Google Ads, Google Shopping, etc.) Universal Results (Featured Snippets, Videos, etc.) Knowledge Graph (Weather, Population, Stock Price, etc.)
Google SERP features are heavily influenced by search intent. For example, searches with transactional intent are typically accompanied by shopping results.
On the other hand, rich snippets and featured snippets mostly show up for searches with informational intent.
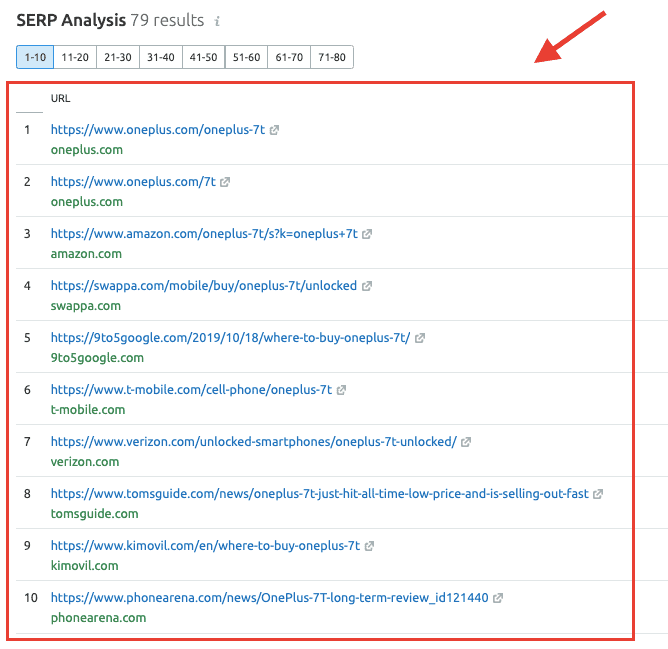
In most cases, you’ll be able to infer search intent of your target keywords by performing a search on Google and scanning through the top-ranking pages. However, Google rankings fluctuate over a period of time. In such instances, I highly recommend you use a tool like SEMrush or Ahrefs to check the ranking history of your target keywords. On SEMrush, you can find the top 10 search results for your target keywords by viewing the SERP Analysis data in the Keyword Overview report. To get this data, enter your target keywords in the SEMrush search box and navigate to Keyword Overview —> SERP Analysis Here you can view the top 10 results for your seed keywords.
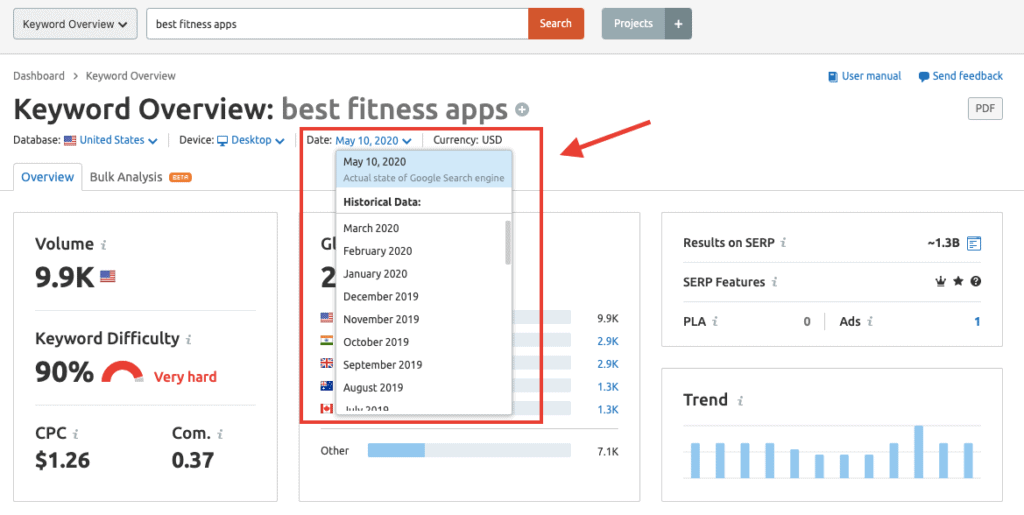
Now, you can view the top 10 search results for your target keyword terms for any past date with SEMrush’s historical data analysis. Historical data within the SEMrush Keyword Analytics toolkit enables you to perform research on keywords on a month-to-month basis dating back to January 2012. To access historical data, you need to click on the date selector at the top of the Keyword Overview report. From the dropdown menu, select the month and year for which you’d like to see the top 10 search results.
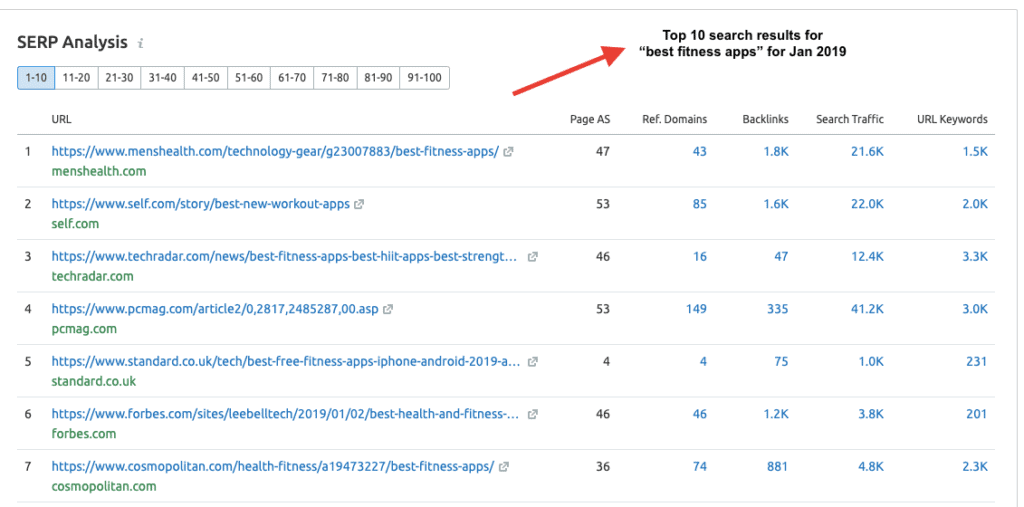
Scroll down to SERP Analysis to find the top 10 search results for your keywords on that particular date and take note of any fluctuations in rankings.
If you notice drastic changes in the top 10 results for your target keywords over a period of time, that means the dominant search intent for the keywords is in a state of flux. In such instances, it’s better to pick different target keyword terms for your content. Note: In order to access historical data, you’ll need SEMrush’s Guru level plan or higher. Click on the link below to get 1-month free access to SEMrush’s Guru plan. Get 1-month free access to SEMrush GURU [worth $199.95]
2. Choose the right content type
Once you’ve zeroed in on your target keywords, the next key step is to decide on the content type. The four content types that dominate SERPs are as follows:
Blog posts eCommerce Category pages Product pages Landing pages
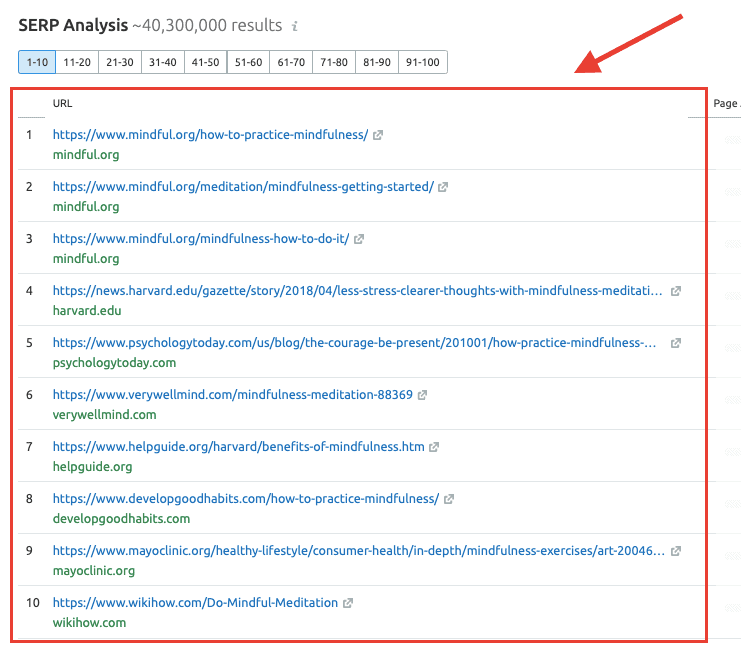
Your target keyword terms will fall under one of these four content types. For example, the top search results for “how to practice mindfulness meditation” are mostly blog posts.
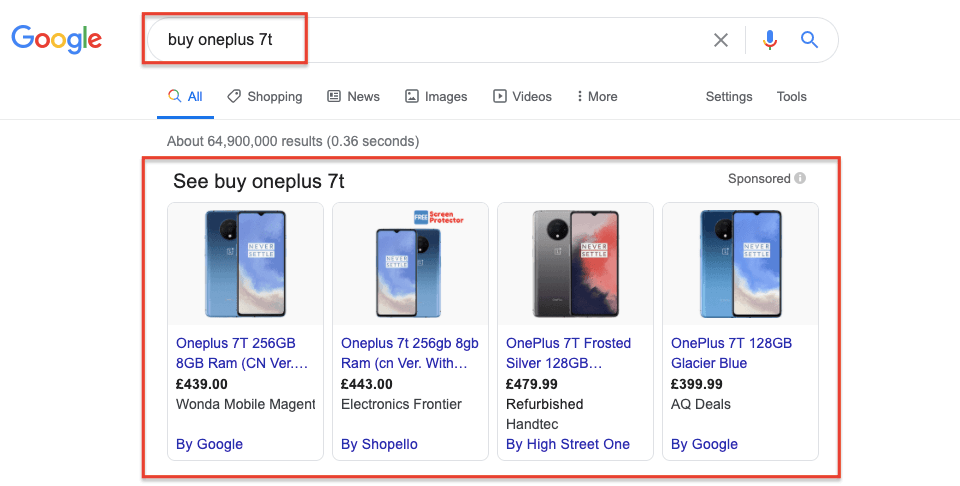
On the other hand, the top search results for “buy oneplus 7t” are all eCommerce category pages or product pages.
Once you’ve identified the content type that’s most likely to rank for your target keywords, it’s time to get started with your content and make sure it aligns with the search intent of the keywords.
3. Update and relaunch existing content
Content relaunch is a highly underrated SEO technique that’s proven invaluable to me ever since I started this blog. Case in point: I was able to increase organic traffic to an old blog post by 146% simply by updating and relaunching it.
Content relaunch is a 5-step process which works as follows:
Identify the post that needs an update Upgrade your content with new information Optimize your target keywords Add new visuals Relaunch the post
When it comes to optimizing pages for search intent, you need to find posts where your content and the search intent behind the target keywords don’t match. You can dig into your archives to see if there are instances where you optimized a page for the wrong search intent. Perhaps there’s a blog post which was wrongly optimized for keywords with transactional intent, when it should have been optimized for commercial intent. Revisit such posts and update them by aligning your content with the search intent. Recommended reading: Content Upgrade Strategy: How to Optimize Old Blog Posts to Get More Traffic
4. Improve the user experience on your website
Google wants users to find the right answers to their queries and have a great experience while doing so. As such, it’s important that you improve the user experience on your website to make sure you start ranking higher for your target keywords. Several factors contribute to bad user experience on your website. Poor site structure, too many broken links, and a slow loading website are just a few factors that can quickly alienate users. Here are a few things you can do to improve your website’s user experience:
Optimize your page speed
Page speed is perhaps the most critical aspect of providing a good user experience to your visitors. As such, Google considers page speed as one of its top ranking factors. Use free tools such as GTMetrix and PageSpeed Insights to constantly monitor your site’s page speed and take action to fix any speed-related issues that come up. Image compression is one of the easiest ways you can speed up your website. Use TinyPNG to compress the images before you upload them to your site.
To further improve your site speed, minify JavaScript and CSS resources, and implement browser cashing. If you have the budget, invest in a caching plugin like WP Rocket to speed up your WordPress site.
Add visuals
Images, screenshots, and videos provide a much-needed visual break from the text for your visitors. So use them strategically within your content to elaborate on some of your points and increase engagement.
You can design your own graphics using DIY tools such as Canva and Venngage. If you have a bigger budget, you can sign up for Design Pickle and get a professional designer assigned to your account for all your design needs. Pricing plans at Design Pickle start from $399/mo.
Use whitespace
Getting the undivided attention of website visitors is easier said than done. Nowadays, users tend to skim posts rather read them entirely. This is where whitespace (empty space between different elements on your site) can be so useful. Effective use of whitespace in your layout can provide that much-needed breathing space to your visitors and make it easier for them to absorb your content.
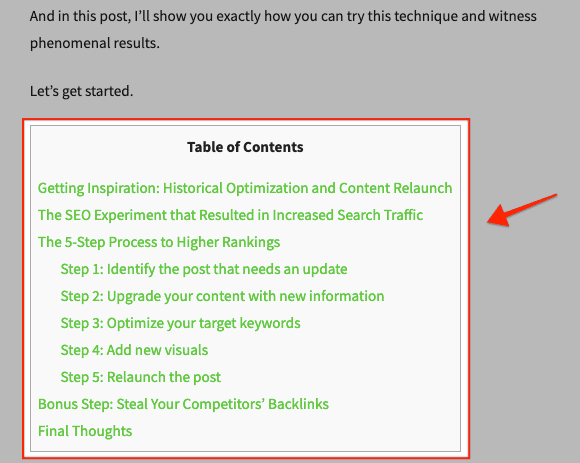
Add Table of Contents
If you publish long-form posts on your blog, you can improve the reading experience of your visitors simply by adding a table of contents to your posts. This will allow them to navigate to sections they’re interested in.
If you use WordPress, you can download and install the free Table of Contents Plus plugin to insert table of contents in your posts.
5. Get constant feedback from your community
Getting honest feedback for your content from your community allows you to learn whether their questions and problems are being answered. If your post is the go-to resource for your target audience for that specific topic, then you’re probably doing a great job aligning your content with the search intent of your target keywords. On the other hand, if your readers highlight certain areas where they need more information, then you can take this new information into account and upgrade your content so that it completely addresses all the questions your readers have regarding the topic. If you don’t already have an active community for your brand on social media, there’s an easy fix: have an active comments section on your blog. Encourage people to comment on your posts and always make it a point to respond to as many comments as possible. Always end a blog post by prompting your readers to leave a comment or ask questions in the comments section.
When you encourage conversations on your blog, you may stumble upon an idea that completely skipped your mind while writing the post.
Final Thoughts
If you’d like to consistently rank higher in Google SERPs, you need to make sure your content matches the search intent of your target keywords. It’s a ranking factor that’s often overlooked, but it’s extremely important. As explained in this post, satisfying search intent of its users is Google’s primary goal. If your content fails to do that, you’ll see your search rankings drop and organic traffic decline. If you liked this article, please share it on Twitter using the link below:
20 Questions to Ask Potential SEO Clients 19 Best SEO Plugins for WordPress How to Create an XML Sitemap for Your Website (and Submit it to Google)