It took years of consistent improvements – to the point where it now receives over 63,000 searches every second. To enhance users’ search experience, Google regularly updates its algorithms. In fact, in 2018 alone, Google dished out over 3,000 different updates.
Download Now: The Ultimate Guide to Link Building – 25 Actionable Strategies to Build High Quality Backlinks [Free eBook]
Most of these annual updates are minor (with some not even confirmed by Google), target specific factors, and at times, leave no significant impact on rankings. However, some of these Google updates – also known as broad core search algorithm updates – are major and have significant implications for digital marketers. These updates are difficult to figure out since Google never really specifies what they target. 2019 has already seen several updates. In this article, we’ll discuss the 3 major changes that were confirmed by Google, and break them down for you. Let’s get started!
1. March 2019 Broad Core Algorithm Update
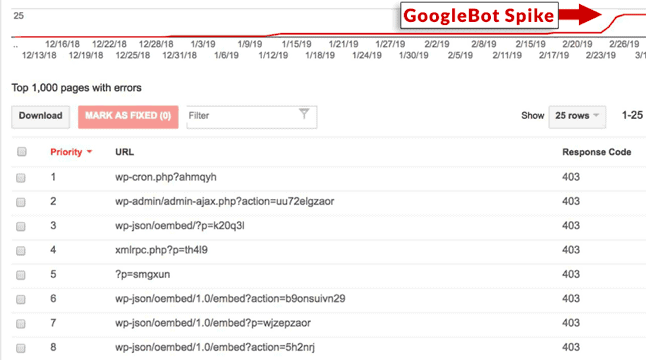
On March 12, Google released its first broad core search algorithm update of 2019. Unofficially known as Florida 2, the update came a few weeks after a surge in Googlebot’s activity and industry chatter were noted.
Source: Search Engine Journal As with every broad core Google algorithm update, initially, the global search community had no clue what the change was actually about. All everyone knew was that the update affected some websites’ rankings. Some webmasters reported an increase in organic traffic overnight. Others, however, weren’t so lucky, as their websites dropped in the SERPs. As usual, Google pointed out that there wasn’t anything in particular to fix.
Speculations and Theories about the Update
After analyzing the data, several experts came forward with their theories on what the March 2019 core Google update targeted. Here are two popular ones that made the final cut:
Bias in favor of authoritative sites
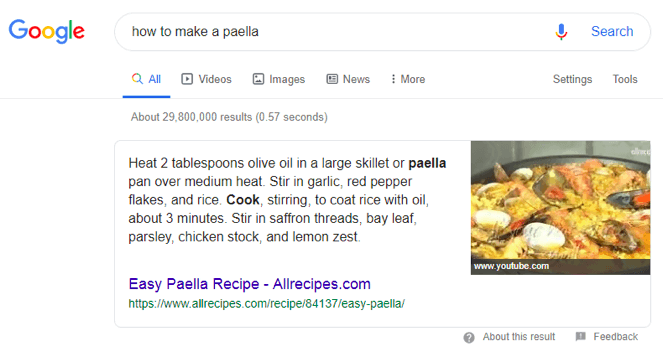
Some experts believe that the March 2019 Google update gave authoritative websites an edge. The update may have allowed popular websites to outrank others for various search queries, regardless of the quality of the content. For example, AllRecipes.com now ranks number one (and shows up as the featured snippet) for the search query ‘how to make paella’.
Here’s the catch – the Paella recipe shared on this page recommends a large portion of chicken and a very small amount of seafood, even though traditionally, Paella is mostly seafood. This could very well be due to the new update. Most users want to read the recipes shared at AllRecipes, regardless of their end-results. This concept is similar to Moz’s domain authority – a metric which Google claims to have never used, even though, at times, the data indicates otherwise.
It might have been a rollback of previous updates
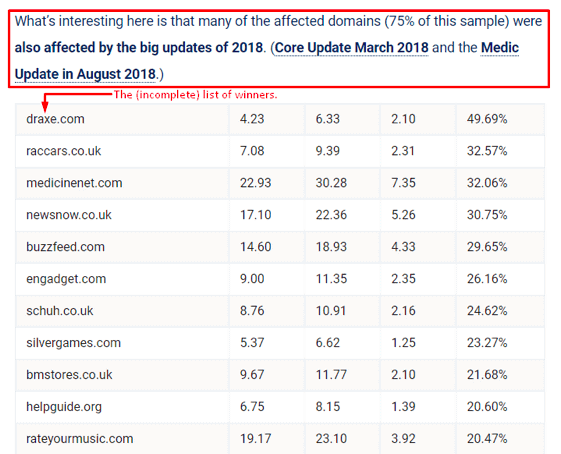
Google essentially uses a trial-and-error approach to improve its complex algorithms. This means that it can reverse previous, supposedly obsolete updates, with a new “update.” Some experts believe that the March 2019 Google update was exactly that – a rollback of some previous changes. Sistrix, a marketing research company, prepared a report on the winners (websites that rose in rankings after the update) and losers (those that didn’t do so well) for this update. The (UK-based) data showed something interesting – approximately 75% of the “winners” were websites that were negatively affected by updates in 2018.
Screenshot of the actual Sistrix article Could this mean that Google reversed some of its previous updates? We’ll never know for sure, because, as mentioned above, broad core algorithm updates target an array of factors, and Google never discloses what those are.
Implications for Marketers
✓ Keep content up-to-date – in an interview with SEJ’s Roger Montti, Jeff Coyle (co-founder, MarketMuse) said that websites with outdated (and low quality) content were hit hard by the March 2019 Google update. This puts more emphasis on producing timeless content and/or updating it from time to time. ✓ Follow a consistent publishing schedule – in the same interview, Coyle indicated that websites that strictly followed a regular publishing schedule, reported few or no negative effects from the update. This provides further proof that it is helpful to consistently publish relevant and valuable content. Doing so could do wonders for your “authority” and help you become the preferred source of content for the average user.
2. June 2019 Core Update
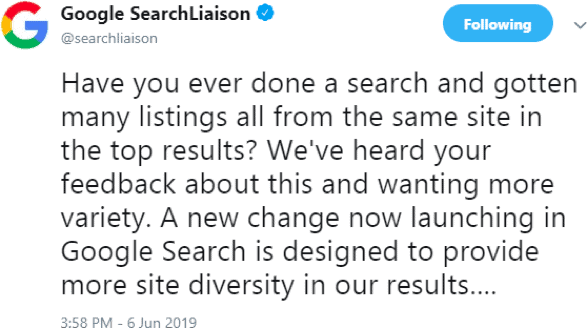
In early June, Google rolled out its second core update of 2019. This large-scale update – which took 5 days (June 3rd till June 8th) to fully take effect – impacted many websites. The update was so significant that even the likes of Daily Mail, with their so-called high authority domains, were negatively affected – receiving a whopping 50% decline in their daily traffic. Some top-performing websites (such as CCN) that were hit by this update even announced that they would shut down. In fact, considering the magnitude of the June 2019 core update, Google gave a heads up to all webmasters with a pre-announcement. The pre-announcement was made by the official Google SearchLiaison Twitter account on 2nd June. Here’s the actual tweet:
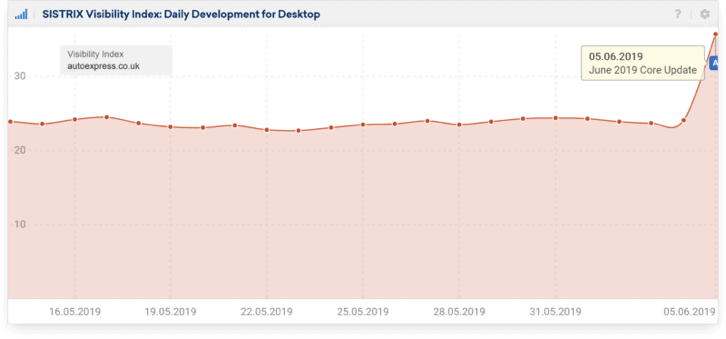
Needless to say, the change was significant. As with every core update, where some websites lost a lot of organic traffic and visibility, others really took off. For reference, see this dramatic change in visibility index for a sample website that took place overnight while the update was rolling out (data by Sistrix):
Speculations and Theories about the Update
So, what was the June 2019 Google core update all about? It’s still too early to tell, but here’s what the data indicates, so far:
Bad word-of-mouth by other big names could mean disaster
Out of all the affected websites of the July 2019 Google update, it seems that Daily Mail has received the most attention. The world was shocked when one of UK’s largest publications lost almost half of its organic traffic. So, what happened to Daily Mail? More importantly, whatever happened to the good ol’ E-A-T (expertise, authority, trust) methodology? It’s hard to doubt the expertise and authority of Daily Mail’s teams. But as far as trustworthiness is concerned – it might not be the publication’s strongest point. The main culprit could’ve been bad word-of-mouth by the following high authority websites, which hurt Daily Mail’s trustworthiness:
MediaBiasFactCheck.com
According to MediaBiasFactCheck.com, a popular platform where users can check the credibility of news and its sources, Daily Mail isn’t reliable. The website says that Daily Mail uses unrealistic and sensationalized headlines to attract readers, and at times, even publishes fake news. MediaBiasFactCheck.com used the headline “Woman, 63, ‘becomes PREGNANT in the mouth’ with baby squid after eating calamari” as an example, stating that this news was “obviously fake.” What they didn’t realize, however, was that this news was 100% real and a woman did discover a baby squid growing in her mouth after eating seafood.
Wikipedia
While Wikipedia is no longer considered a credible source of information, a lot of people still turn to it to get the gist of broad topics. The Wikipedia page on the Daily Mail says that the publication has been criticized for being an unreliable source of information.
Screenshot of Wikipedia’s page on the Daily Mail
Politifact
Another website, Politifact (a platform for double-checking the claims of politicians and other authority figures, as well as, media outlets) also didn’t do the Daily Mail any favors. The website said that one Daily Mail article about Brexit was click-bait.
Another crack at health and YMYL sites
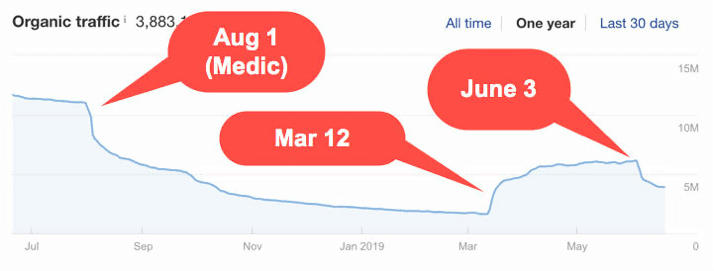
The August 1st, 2018 Google core update (also known as the Medic update) impacted a number of health-based, and some other YMYL (your money or your life) websites. Organic traffic on these websites dropped drastically, as did their rankings. Google’s aim was to protect users from (possibly) inaccurate medical and financial advice. Naturally, websites which had problems with online reputation were hit the hardest. However, the March 2019 update, which felt like a rollback, gave these websites a slight boost in organic traffic. Sadly, it didn’t last long, as they were hit yet again by the June 2019 core update. The following screenshot by Marie Haynes Consulting shows the fall, rise, and second fall of these websites:
Implications for Marketers
✓ Focus on online reputation management – before the June 2019 update, the general belief was that the big players had nothing to fear from a few bad reviews/articles. However, considering what happened to the Daily Mail, things have changed. Websites, big or small, now have to invest heavily in online reputation management. The following is how you can achieve that:
Come forward with a clarification every time a website questions your credibility. If reasonable, respectfully ask such websites to take down the bad claim. As a last resort, you could consider taking legal action against a website that has shared fake/unreasonable negative reviews about you. If you run a news website, try taking sensational headlines down a notch. Doing so could prevent people from assuming that you’re publishing fake news.
✓ Develop trust – since trust matters a lot to users (regardless of whether or not Google actually uses it as a direct metric/factor), it’s about time you started to build some. This especially applies to health websites. Here are some tips to help you out:
Provide ample amount of citations for grand claims. Use reliable sources. If possible, don’t disagree from the general medical/scientific consensus (this may be challenging for websites selling natural/non-synthetic remedies).
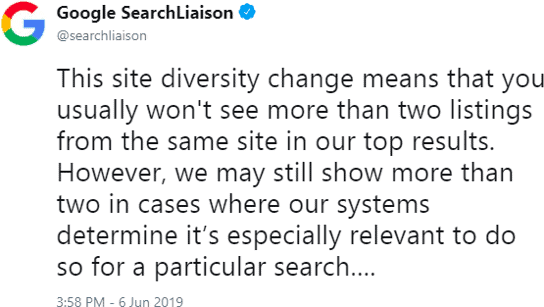
3. June 6 Site Diversity Google Update
The June 2019 core update wasn’t the only center of attention during the month. While the core update was rolling out, Google announced another update on June 6th. Called the Diversity Update, it was focused on displaying more diverse results.
Source It’s still not clear whether the timing of this update was intentional or pure coincidence. In any case, this clash of the June core update and the ‘site diversity’ updates made things a lot more complicated for analysts. To summarize – Google will no longer display more than two results from the same domain on most SERPs. The aim is to encourage content marketers to produce unique content and promote a fair division of organic traffic.
Speculations and Theories about the Update
There isn’t anything much to speculate about the site diversity update. However, there’s one interesting take that’s worth mentioning:
The diversity update is only a PR move
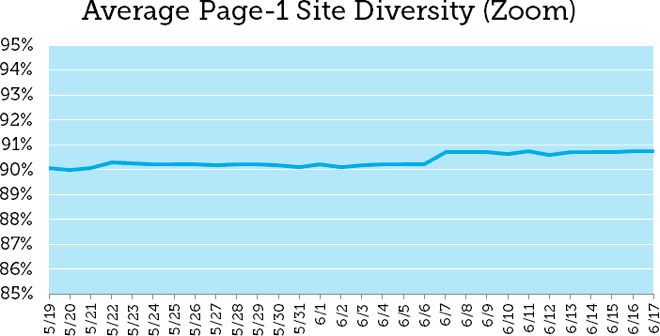
In a recent article, Dr. Peter J. Meyers of Moz made a point about the Google site diversity update. After analyzing a set of 10,000 keywords and taking an average of page diversity, he found that the update didn’t really live up to expectations. By June 7, the average site diversity on page-1 increased by a mere 0.49% (from 90.23% to 90.72%). This chart shows the marginal change:
Source As you can see, after the small rise in diversity (which occurred between 6th and 7th June), the line stays almost flat. However, to be clear, Google did point out that it was still possible for a domain to get more than two results on a SERP.
Source Dr. Meyers dug deeper and looked at SERPs with more than two results of the same domain and a diversity score of more than 80%. The post-update data showed a rise in just 2.1% in diversity, which is still not very impressive. Could this mean that the site diversity update was no more than a PR stunt? It’s hard to say, but considering the marginal changes, it could very well have been.
Implications for Marketers
So, does the site diversity update mean that you need to start looking for additional domain names and reading domain hosting service reviews? No, as that would be an incorrect approach within this specific update. Assuming that you were getting more than 2 listings on SERPs for specific queries, you don’t need to worry, as you won’t lose any (significant) amount of organic traffic. If anything, this could help you attract more qualified traffic. Here are some tips on how to benefit from the diversity update:
If one of your pages was moved from the first SERP after the site diversity update, internally link it from the pages that are still ranking. Optimize your landing pages for featured snippets to improve your odds of getting more clicks, rather than relying on multiple listings per SERP.
Conclusion
Considering the 2019 Google updates discussed above, it’s safe to say that SEO experts need to better and more quickly adapt to changing trends. What works today, might not work tomorrow. The three take-home messages are; to stay up-to-speed with the latest updates, keep an ear out for industry chatter on any possible changes (use social listening tools if you must and follow industry leaders) and analyze the data before coming to a conclusion. Found this article useful? Please share it on Twitter using the link below: [ctt template=”3″ link=”91CDP” via=”no” ]Google Updates in 2019 – A Quick Recap[/ctt]
10 Actionable Things You Can Do with SEMrush to Boost Your Traffic Image SEO: 7 Actionable Tips to Supercharge Your Organic Traffic 35+ Best Free SEO Tools to Instantly Boost Your Rankings